A maintenance-free, compact, and energy-efficient water recycling system that achieves a water recycling rate of 85% or more
Kurita Water Industries Ltd. has received an order from Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) for the manufacture of a flight model of the company's next generation water recycling and demonstration system in October 2015. This system is scheduled to be installed in the Japanese Experiment Module "Kibo" on the International Space Station.
Since entering a research agreement with JAXA in 2011 to study future-type water recycling systems, Kurita has conducted research on the elemental technology and treatment methods for a water recycling system that can recycle water (urine) from the inside of the International Space Station (ISS) and stably transform it into drinking water. The flight model ordered by JAXA will be sent to the ISS in 2016 for a demonstration test in the Japanese Experiment Module "Kibo" to be conducted by JAXA. Kurita will also participate in the demonstration test to help it develop a better system.
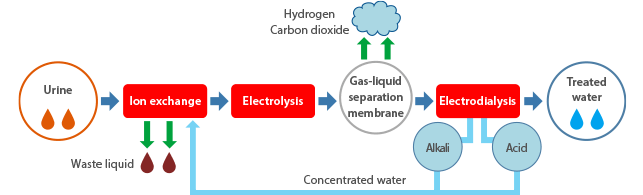
The next generation water recycling and demonstration system ordered by JAXA consists of a control system and a water treatment system made up of ion exchange units, electrolysis units and electrodialysis units. To transform urine into purified drinking water, the system removes calcium and magnesium components from the urine through ion exchange, electrolyzes the organic substances using Kurita's own special electrodes, and then removes the ions by means of electrodialysis. Electrolysis is carried out under high temperature and high pressure to break down organic matter that is difficult to decompose. The safety of the system operating under conditions similar to that of the ISS condition was verified over the course of four years of joint study with JAXA, and the system specifications were finalized.
This new system recycles water at a higher level (a water recycling rate of 85% or more) than the water recycling systems currently used on the ISS. It also consumes about one-half of the power and is one-quarter the size and weight of the current systems. Another added benefit of the new system is that it does not require any maintenance. The regeneration of ion exchange resins is self-contained inside the system, and there is no need to replace the resins.
Currently the ISS uses USA-made and Russian-made water recycling systems. JAXA and Kurita aim to produce an original Japanese water recycling system that is robust and capable of long-term operation in outer space. The next generation water recycling system is expected to play a part in future space activities.
Kurita will continue its pursuit of world-leading water technology developed by industries in the cutting-edge field of space technology development, preparing for the future commercialization of human space exploration.
Reference: Demonstration system on the ground

External view

Inside of the system
Specifications and Features of the Next Generation Water Recycling and Demonstration System
Treatment method (system flow)
- Ion exchange unit
Magnesium and calcium components in the urine are removed through the ion exchange reaction caused by the cation exchange resin. This prevents the adhesion and deposition of water-insoluble components (scale trouble) in the later stages. - Electrolysis unit
The organic compounds in the ion exchange water are decomposed by the oxidizing substances created by the electrolysis of water. - Electrodialysis unit
The remaining ions from the previous process are removed by the ion exchange film that allows only specific ions to pass through. This leaves treated water that is of drinkable level quality.
In addition, the remaining ions are separated into cations and anions to produce acid and alkali. These are used to regenerate ion exchange resins.
Treatment capacity
1 liter per day
Water recycling rate
85% or more
Specifications
- Water treatment system
Material: Aluminum
Dimension: W 535 mm x D 600 mm x H 480 mm - Control system
Material: Aluminum
Dimension: W 120 mm x D 580 mm x H 475 mm