Basic Concept
The Kurita Group views climate change as an urgent issue that needs to be addressed globally, and based on the TCFD Recommendations, we will continuously reduce greenhouse gases generated by our business activities and contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions for our customers through our business.
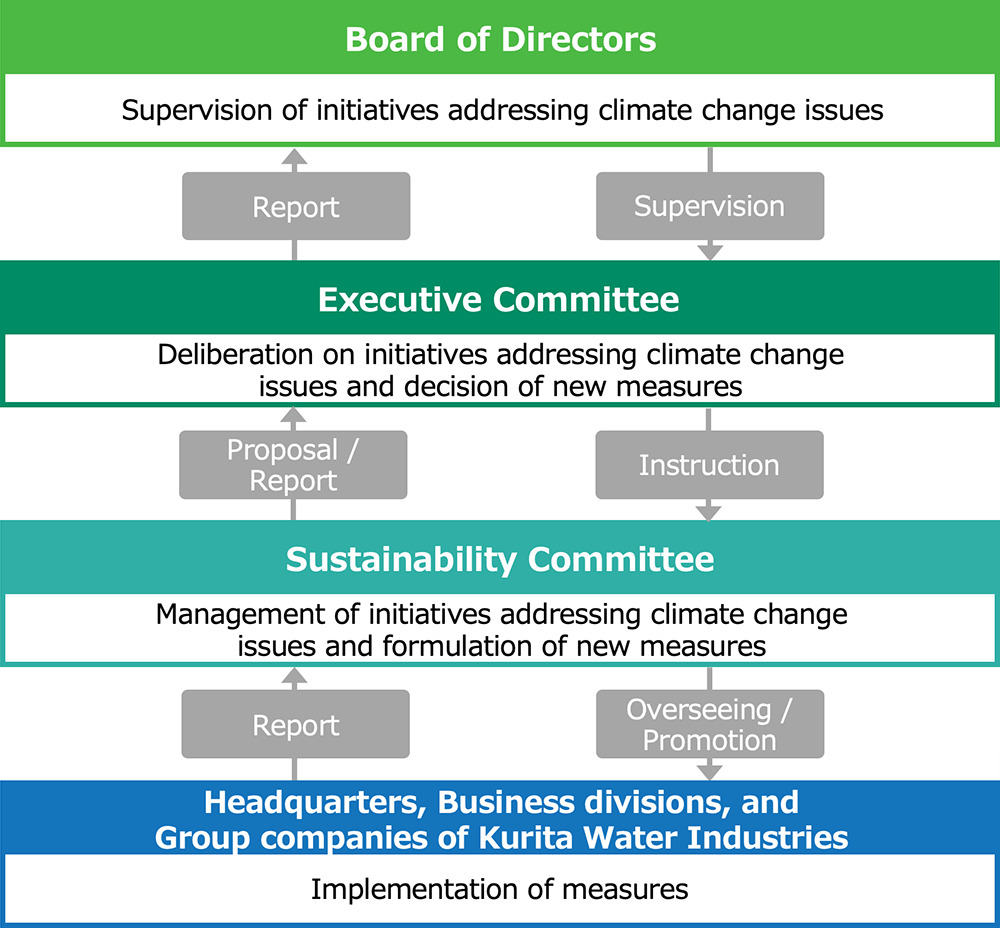
Promotion System
The Kurita Group sets the Sustainability Committee, chaired by Executive General Manager of Sustainability Division and Executive Officer of Kurita Water Industries, which oversees and promotes initiatves addressing climate change. The Board of Directors supervises the initiatives, receives reports from the Executive Committee twice a year in principle. The Executive Committee receives reports from the Sustainability Committee on the status of efforts to address climate change issues, deliberates on the details, and determines necessary measures.
Measures Based on Opportunities and Risks
Based on the two scenarios (1.5℃ and 4℃)*1 described in IPCC SR1.5 and IPCC RCP8.5, etc. the Kurita Group has evaluated the risks and opportunities by two axes of “probability” and “impact” for short-term, medium-term and long-term*2, and has formulated the measures of the Kurita Group as well as evaluating the financial impacts on our business for some of them.
| Type | Risks and Opportunities | Time horizon | Financial Impact/Measures | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Policy and Legal | Risk | Introduction or increase of carbon tax. | Med to long term |
<Financial Impact (As FY2051)>
<Measures>
|
| Risk | Regulations for products and services with high GHG emissions. | Med to long term |
<Measures>
|
|
| Opportunity | Dissemination of supportive policy incentives to the conversion to energy with low GHG emissions. | Med to long term | ||
| Technology | Risk / Opportunity |
Substitution of existing products and services with lower emissions options. | Short to long term | |
| Market | Risk | Decreased demand from fossil fuel-related sector. | Med to long term |
<Measures>
|
| Risk | Soaring costs of material and energy. | Med to long term |
<Measures>
|
|
| Opportunity | Increased demand in the electronic industry due to the acceleration of DX. | Med to long term | ||
| Physical Risks | Risk | Increased factory shutdowns and construction delays due to extreme weather events such as cyclones and floods. | Short to long term |
<Financial Impact (After FY2021)>
<Measures>
|
| Opportunity | Increased operating rate of cooling equipment. | Short to long term |
<Measures>
|
|
| Resource Efficiency | Opportunity | Dissemination of efficient production and distribution processes. | Short to long term | |
| Opportunity | Reduction of water usage. | Short to long term | ||
| Energy Source | Opportunity | Dissemination of energy with low GHG emissions. | Short to long term | |
| Opportunity | Conversion to distributed energy resources. | Short to long term | ||
| Products and Services | Opportunity | Increased demand for products and services with low GHG emissions. | Short to long term |
<Financial Impact After (FY2028)>
<Measures>
|
| Opportunity | Increasing diverse technical needs for reducing GHG emissions. | Short to long term | ||
| Resilience | Risk/ Opportunity |
Substitution and diversification of fuel and water resources. | Short to long term |
<Measures>
|
- *1 The scenario in which the temperature rise from the pre-industrial level is 1.5℃ and the scenario with the highest temperature rise predicted by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.
- *2 Short-term (1-3 years), medium-term (3-5 years) and long-term (5-20 years).
- *3 (Scope 1 and 2 + Scope 3 category 1 in the business operation area) x (Carbon price in the business operation area) estimated based on the FY2051 forecast.
- *4 Products, technologies, and business models that contribute to saving water, reducing GHG emissions, recycling waste into resources and reducing resource inputs more greatly than conventional ones.
- *5 Trial calculation of SAM (Serviceable Available Market) for new CSV business that contributes to GHG reduction.
Metrics and Targets
To promote sustainability initiatives, the Kurita Group has identified eight new
themes to intensively work on from FY2024 as the “Kurita Group Materiality.” In
Theme 2, which is an initiative to tackle climate change issue, in order to make
efforts in line with the Paris Agreement, we have set new long-term targets aligned
with “Net-Zero target” indicated by SBTi*, starting from FY2020 as the
baseline year, and are working to reduce Scope 1, 2 and Scope 3 emissions.
In addition, we have set a new medium-term target for the amount of avoided GHG
emissions through CSV business and we will realize a decarbonized society throughout
the entire supply chain by developing and providing low-carbon solutions that
contribute to reduction of GHG emissions in industry and society.
In FY2022, Scope 1+2 emissions increased slightly year-on-year due to an increase in
the operation of production bases because of recovery in demand. On the other hand,
Scope 3 emissions decreased year-on-year due to a decline in procurement of pumps,
which are the main source of emissions. In FY2023, Scope 1+2 is expected to decrease
year-on-year due to the implementation of the above measures, while Scope 3 is
expected to increase because the increase due to orders increase will exceed the
reduction by the above measures.
- * An initiative that encourages companies to set reduction targets consistent with scientific knowledge, with the goal of limiting the increase in global average temperature caused by climate change to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels.
| Materiality | Metrics | Medium- and long-term targets* | Achievement* | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FY2028 | FY2031 | FY2051 | FY2020 | FY2021 | FY2022 | ||
| 2. Contribution to the realization of a decarbonized society | Scope 1+2 | 73% | 100% | Net-Zero |
- (44 thousand t-CO2) |
7% (41 thousand t-CO2) |
5% (42 thousand t-CO2) |
| Scope 3 | 22% | 30% | Net-Zero |
- (2,584 thousand t-CO2) |
6% (2,440 thousand t-CO2) |
22% (2,027 thousand t-CO2) |
|
| Avoided GHG emissions through CSV business |
1,500 thousand t-CO2 |
- | - |
279 thousand t-CO2 |
294 thousand t-CO2 |
367 thousand t-CO2 |
|
- * Scope 1+2 and 3 are reduction rates from FY2020 (base year).
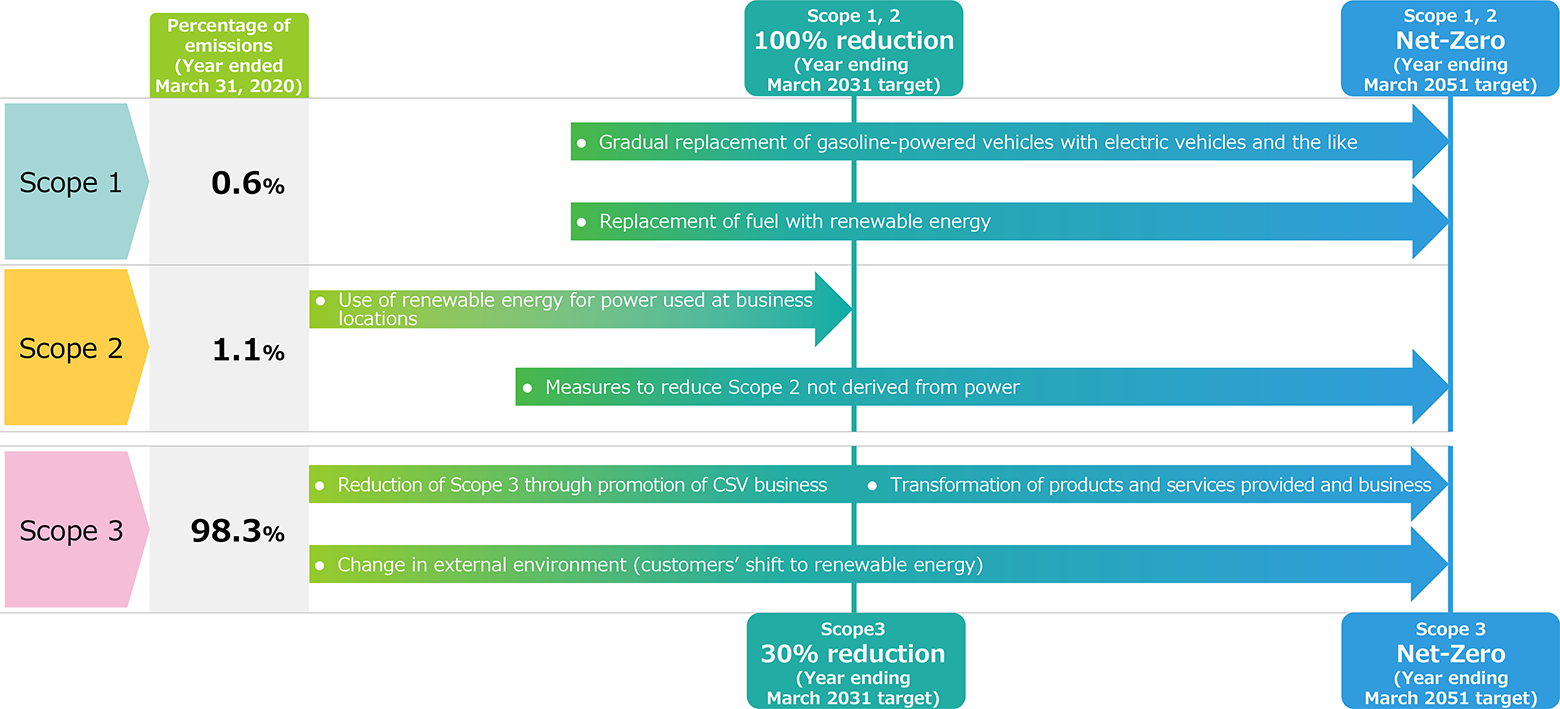
Emissions Reduction Plans to Achieve Scope 1, 2 and 3 Targets
The Kurita Group’s CO2 emissions in FY2020, the base year for the metrics, were approximately 2% for Scope 1 and 2 and 98% for Scope 3. Scope 1 and 2 are mostly derived from Scope 2 electricity. We will therefore promote the switch to electricity derived from renewable energy and gradually switch from gasoline cars to electric cars. In Scope 3, about 70% of the emissions are from Category 11, “Use of sold products (mainly rotating machinery such as pumps used to pump water).” To maintain a balance with increasing our competitive strength, the Kurita Group will use its CSV business structure to provide low carbon solutions to our customers.
The Kurita Group’s report based on the TCFD recommendations.